Table of Contents
-
Focus on high-authority, relevant backlinks that align with SEO goals and user value.
-
Evaluate link quality using DA/DR, PA/UR, relevancy, organic traffic, and spam metrics.
-
Prioritize natural link acquisition patterns and avoid spammy or paid link services.
-
Use evergreen strategies like data studies, guest posts, and reactive PR for scalable link building.
-
Apply Google’s E-E-A-T and Helpful Content principles to assess link source trustworthiness.
-
Track link effectiveness with tools like Ahrefs, Moz, and Majestic to refine your strategy.
Quality vs quantity. The age-old question.
Most SEOs want to scale their processes, but it’s virtually impossible to scale link building while ensuring quality.
As brands constantly ask how many links they need to build, the question should be, how many quality links do I need to build?
Quality may differ depending on the site’s goal, but backlinks should always drive value. And value comes from quality.
Let’s dig deeper into quality backlinks, what to look for, and strategies you can employ to build them.
What Makes a Link “Quality”?
A quality link is a mid to high-authority link relevant to your business.
However, quality might mean many different things to different people at a company. Some stakeholders may want news mentions; others may need backlinks that lead to conversions.
In this post, we are talking about link quality from an SEO perspective.
The terms authority and relevancy deserve some specific consideration, however. In our post about relevant links, we shared a matrix about authority and relevancy, which is essential to understand when discussing quality.
Here are some simple ways to gauge link quality based on quantitative and qualitative factors. Base your overall link quality assessment on a mix of the following:
High Site Relevancy
A quality link is also from a site relevant to your niche. There are certainly degrees of relevancy, but the further away from a core offering you get, the less valuable the link becomes.
Remember, links serve as an authority signal. When other relevant sites in your niche signal that your site is an authority for a topic with a link, Google will perceive you as an authority.
The other reason is that a relevant link brings relevant traffic to your site, which could lead to sales or other positive customer interactions like comments or shares.
Read our post about relevant links to get a complete picture of what makes a site relevant.
Note: If you create off-topic content and get links from the same off-topic sites, this doesn’t help your case for SEO. If anything, it will confuse Google.
High Domain Authority or Domain Rating
Domain Authority (DA) is a proprietary metric from Moz based on signals like backlinks and site traffic. The metrics emulate Google’s PageRank system. Domain Rating (DR) is a similar metric from Ahrefs, though theirs comes from a site’s backlink profile. Both have a 100-point scale.
Look for sites at least above ~60 DA/DR.
Note: A brand new site may not have as high of a DA/DR because they’ve just launched. Don’t discount them immediately if the site is relevant and trustworthy. They may just need time to grow their authority.
High Estimated Sitewide Organic Traffic
You won’t be able to tell the actual monthly traffic with any tools, but most can give you estimated organic traffic.
Sites above 5K~10K monthly organic traffic are of average quality.
Use a tool like Ahrefs Site Explorer to see the organic site traffic.
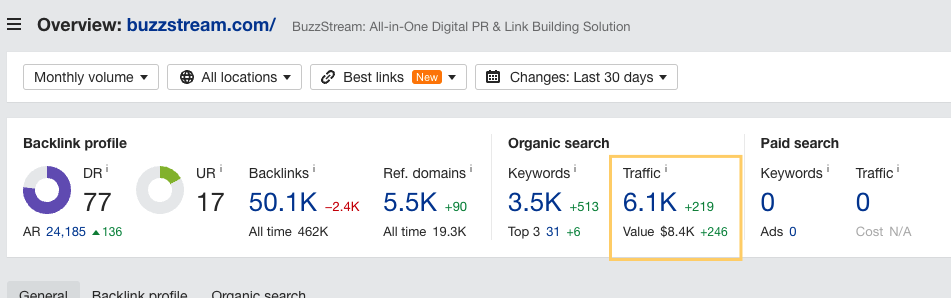
In the example above, the monthly estimated organic traffic is 6,100 visits.
Above Average Page Authority or URL Rating
Page Authority (PA) is Moz’s measure of a page’s ability to rank based on several factors, and URL Rating (UR) is Ahref’s based again on the strength of the backlink profile. Both are on a 100-point scale.
When you get to the page level, metrics can drop. Some top-quality sites have pages with lower page authority or URL rating scores (as compared to their DA/DR).
For example, this page from Whitehouse.gov, which has a DR of 91, has a UR of just 37.

If you’re unsure what an average is in your niche, compare PA/UR to similar sites. For example, if the target link you are evaluating has a UR of 10, but the other similar sites have a UR of 30, then yours is fairly low quality compared. But if
Normal Link Acquisition Velocity
Another interesting concept to consider is the rate at which the site has gotten backlinks. Google doesn’t like when sites acquire sudden bursts of links because it can signal spammy tactics (even if the site got them naturally).
Using a tool like Ahrefs Site Explorer, you can see the progression of a link profile over time. Below is an example of a site with some abnormal link growth.

You want to see a linear movement up and to the right. This represents a natural link growth over time, which Google wants.

Note: Some unnatural spikes may be due to Ahrefs indexing changes. You can compare to other sites in the same niche to see if they saw similar growth simultaneously. Ahrefs is also good at noting these indexing updates.
Low Spam Score
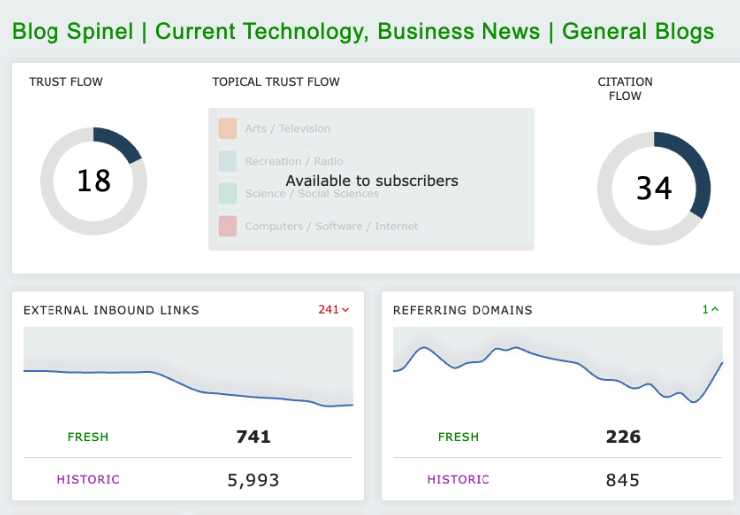
Another way to judge quality would be to look at the backlink profile of the target site with a metric like Moz’s Spam Score, which is part of their Link Explorer.
Spam Score can tell you the likelihood of a site being penalized by Google for spammy tactics.
Another is Majestic’s Trust Flow metric from their Site Explorer Tool.
Lower Number of Outbound Links
Outbound links are crucial for SEO. They can help Google and users better understand what a page is about and help make your page more authoritative.
However, with too many outbound links, a page passes a lower link value to each external page.
Think about outbound links like slices of pie. The website’s total available link value is the whole pie. The more outbound links it has, the smaller the slices each person receives.
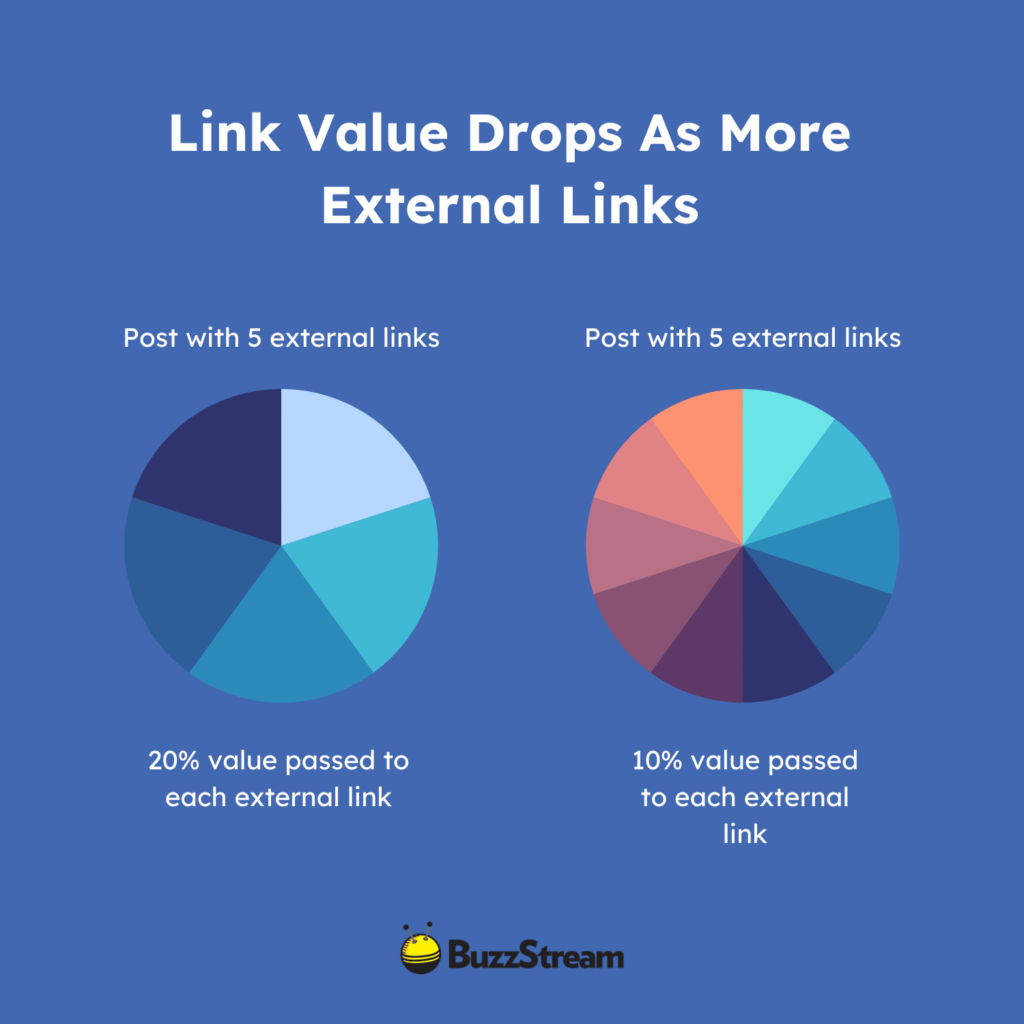
There is no magic number here, but Google once said a site should have fewer than 100 links on a page. Realistically, the number of links where link dilution becomes a problem is probably higher than 100, but keeping an eye on outbound linking practices is important.
It gets genuinely impactful when the outbound links aren’t relevant to the post. Non-relevant links are usually clear signals that a site might be selling links or part of a link farm.
Few Clicks From the Homepage
Aim for links up to ~2-3 clicks from the homepage.
The deeper a page is from the homepage, the less likely it is to get crawled frequently, which means the value may not reach your site.
For example, this post is two clicks from the homepage. A user clicks into our blog home and then the featured quality links post.
You can check the “click depth” with a tool like Screaming Frog or count the clicks yourself.
Displays E-E-A-T Practices and Helpful Content
While Google has insisted that E-E-A-T isn’t a ranking signal, the concept behind a website that displays expertise, experience, authority, and trust will still indirectly impact user engagement, affecting rankings.
Simply put, why would anyone read what a site says if they aren’t putting out authoritative content that people can trust?
Your Money Your Life (Y-M-Y-L) sites are critiqued even closer for proper E-E-A-T characteristics for Google’s search quality raters per their guidelines.
Evaluate the site in the same way that a quality rater would:
- Is the information on the page properly sourced from other authoritative sources?
- Is the person writing someone with experience in the topic?
- Can you trust what they are saying?
Google also asks sites to produce Helpful Content, which pushes creating quality, people-first content. They offer helpful questions to ask, such as:
- Does it provide original information, reporting, research, or analysis?
- Is there a substantial, complete description of the topic?
- Does it offer insightful analysis or interesting information beyond the obvious?
- If using other sources, does it add substantial value and originality?
- Is the heading or title descriptive and helpful without being clickbait?
- Would you bookmark or share this content?
- Could you see this content in a printed magazine, encyclopedia, or book?
These are all qualitative assessments. So, take them as such.
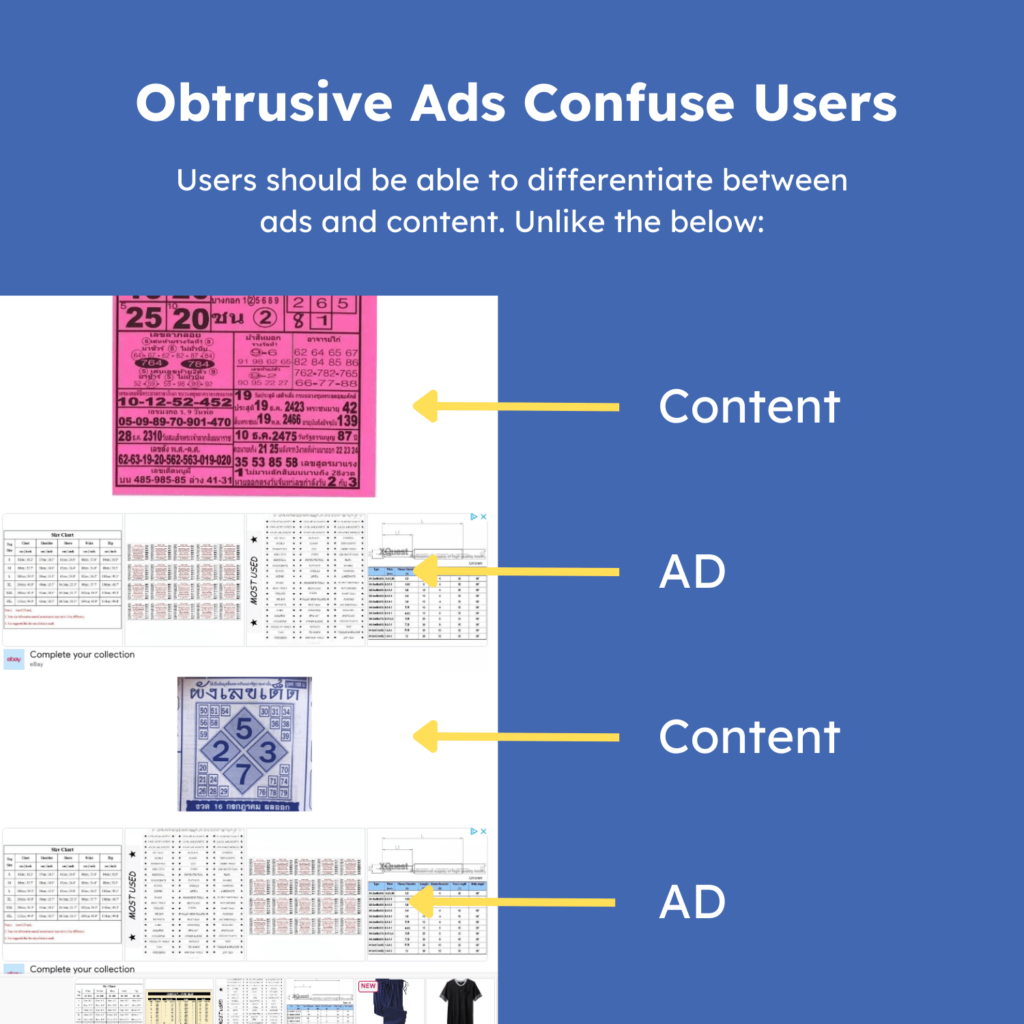
Unobtrusive Ads
In short, ads that cover the content are frowned upon by Google. Does this impact link quality? If the site gets penalized, then yes, it will. However, significant publications rank well where ads are typically found all over the page, which can be somewhat confusing.
So, how should you evaluate ads?
Look to see if you can quickly tell the difference between ads and content on the page. For example, in the image below, the page is so riddled with ads that you can barely tell what is an image from the post and what is an ad.
Quality Link Checklist
So, the checklist for determining whether a link is high quality or not comes down to something like this:
- High DA/DR
- High PA/UR
- High Organic Traffic
- Low Spam Score
- High Site Relevancy
- Low Outbound Links
- Few Clicks from Homepage
- Normal Link Acquisition Velocity
- Display E-E-A-T & Helpful Content
- Unobtrusive Ads
Are there more checks you could do? With this, you can get deep into the weeds, but the list above represents something you can do relatively quickly while evaluating. But your time is better spent writing better content.

When in doubt, use your gut.
If you get a link from a site that doesn’t look great or isn’t writing great content, it’s probably not quality.
High Quality vs Low Quality Links
A low-quality link does not provide value to the user. Google lays out a long list of link spam policies. Essentially, these policies focus on buying or selling links to manipulate rankings, such as paying for links, exchanging products for links, or engaging in excessive link swaps.
Automated link creation and non-disclosed paid links in content also breach these rules. Practices like embedding low-quality or hidden links in widgets, distributing them across multiple sites, or using keyword-rich links in site footers or templates are all frowned upon.
If that’s too much for you, a good rule of thumb is to ask yourself, “Would I be happy with this linking site if it was my own?”
How to Get Quality Links Using These 8 Tactics
Building quality links doesn’t have to be complicated. It simply takes some strategic planning. You can build quality links once you’ve established your industry and niche.
Then it’s just a matter of getting your team together. You can build links with content-led approaches or without content.
Building and Pitching New Content
New, fresh content is one of the best ways to get quality links. But, unless you are a major brand or publication, you’ll need to promote your content to get it seen.
Why?
As the old saying goes, if a tree falls in the forest but there’s no one there to hear it, will it make a sound? The same goes for content. You can build the best content in the world, but it won’t get you any links if no one sees it.
Here are some ways to build new content for pitching.
Lean on Competitors for Inspiration
I always begin my ideation process by looking at what my competitors have done that has gotten them quality links and doing something better.
By leaning on your competitor’s successes, you can estimate ROI, which can get buy-in from clients or C-Suites.
You also have a built-in outreach market if you promote your content. Simply look at the people who have linked to your competitors and reach out with your new, better content.
Use a tool like Ahref’s Content Explorer to find posts with many links in your niche. For example, here’s a search around link-building-related content in BuzzStream’s industry.
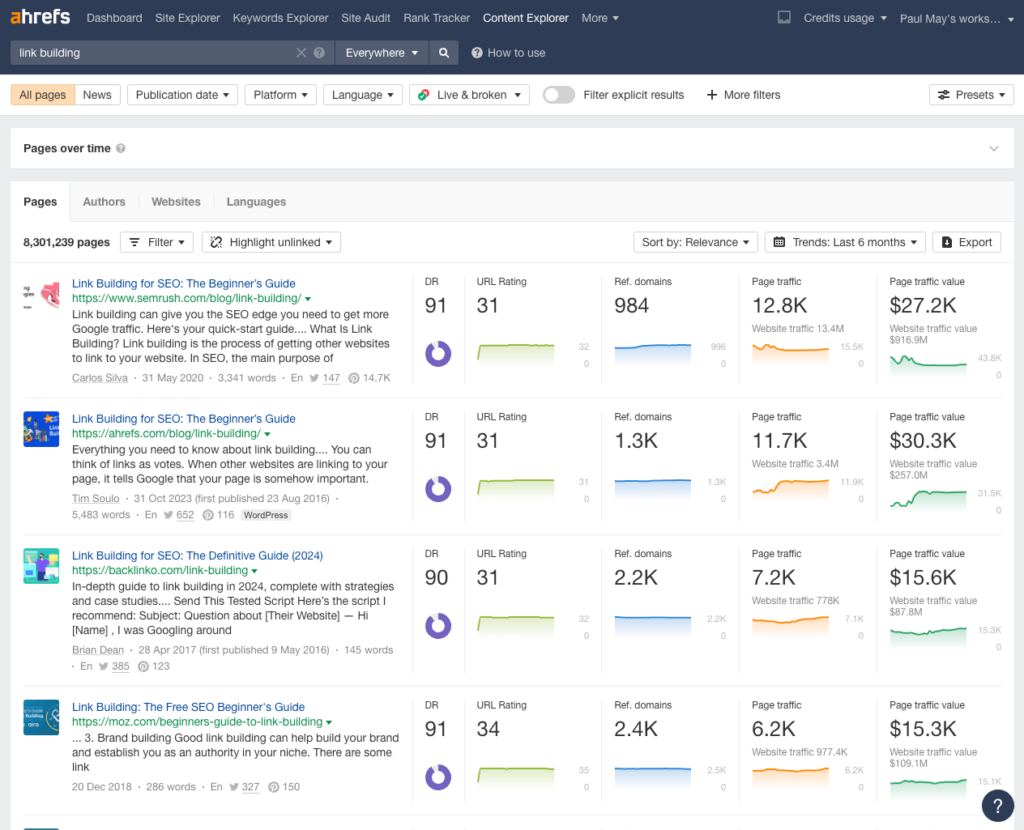
Then you can take an idea that has worked well for your competition, iterate on it, and pitch it for coverage.
Or, if you know of a competitor already in your industry, use the Site Explorer and look at their Top Content.
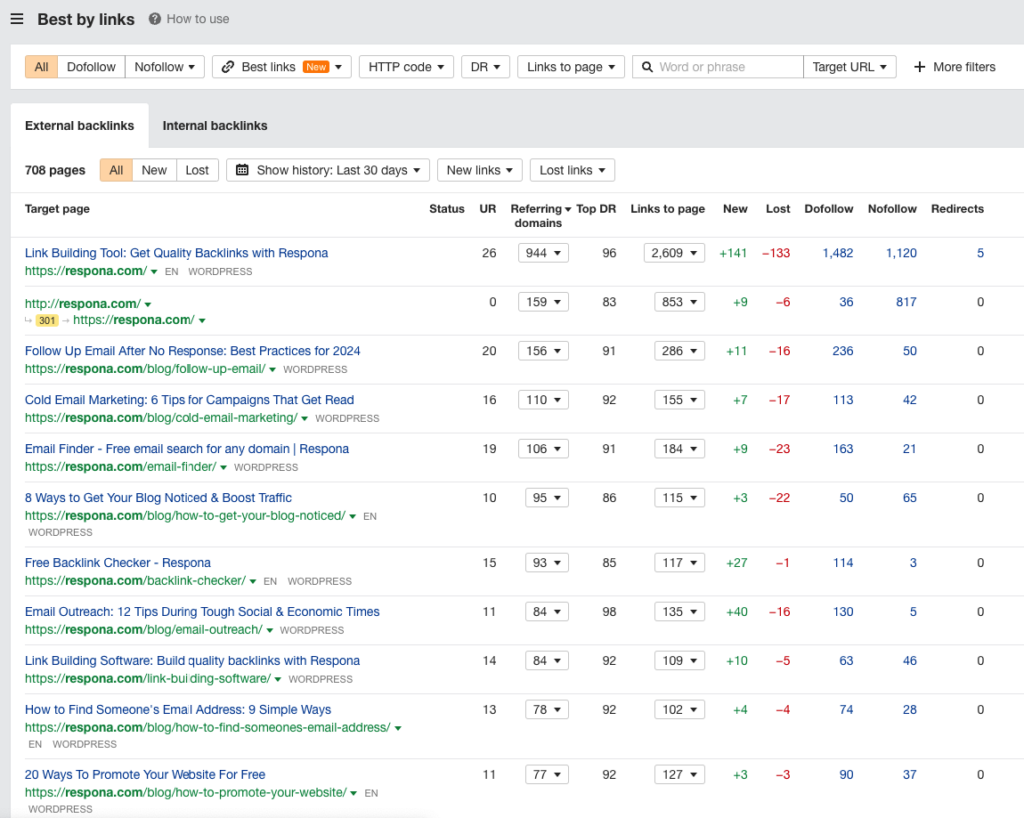
In the image above, I see several posts with many referring domains. Those represent ideas that I know already work.
Create Surveys and Data Studies
Proprietary data is a game-changer for getting links. Creating surveys and data studies is one of the most effective white hat link building tactics today.
If you don’t have access to your own data, you can use a third-party tool like OnePoll or a cheaper option like Pollfish.
Then, it’s a matter of finding linkable angles for your data. Extreme emotions like surprise, anger, and joy all help make a post linkable.
For example, here’s a post from Preply that looked at the cities that swear the most.
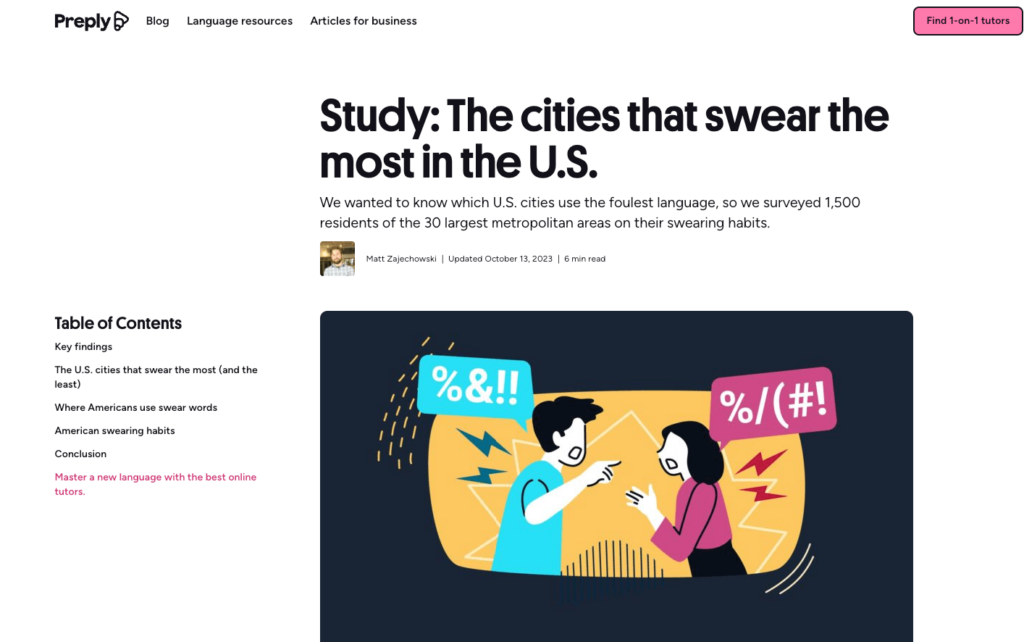
This post yielded over 150 Linking root domains (LRD), including quality links from NYPost and TheHill.
Create Shareable Graphics
One way to make a post more shareable and linkable is by providing a graphic asset that others can refer to in their own posts. Maps, “re-imagined as” concepts, and traditional infographics all fall under that shareable graphic bucket.
Many tools, like Visme or Canva, help create graphics, but visual creativity is the best differentiating factor for graphics. We recommend getting a graphic designer to take your assets to the next level.
For example, Crossword-Solver shared the most-used emoji on Twitter with a highly intricate map:
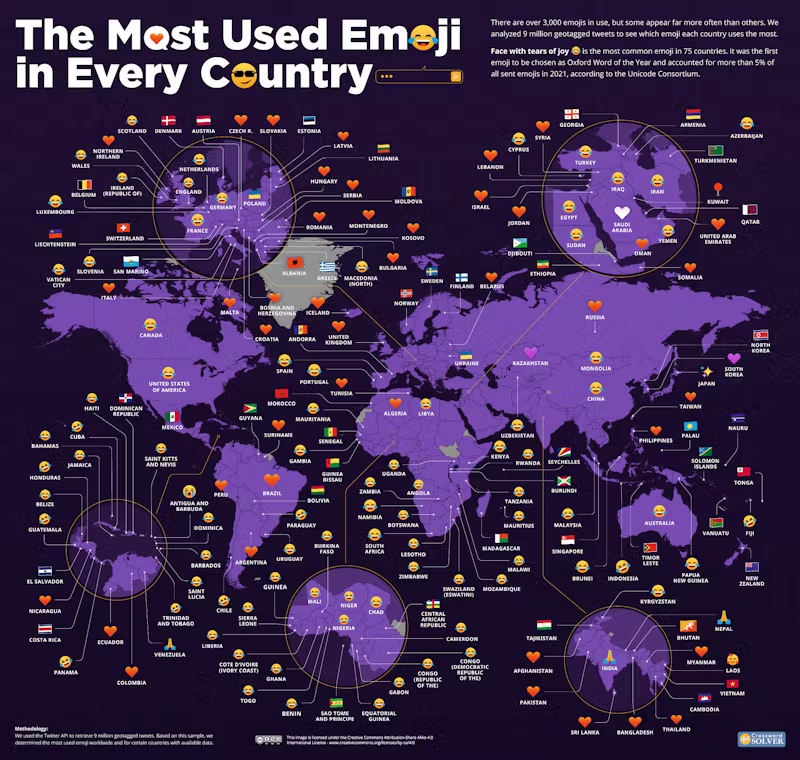
The map post earned them coverage from a high-quality site like PCMag.
Create Interactives and Calculators
Interactives and calculators can be expensive assets to create, but they can yield many high-quality links over time — especially when tied to keywords.
For example, this Student Loan Repayment Calculator from Smart Asset has gained 740 links over time.
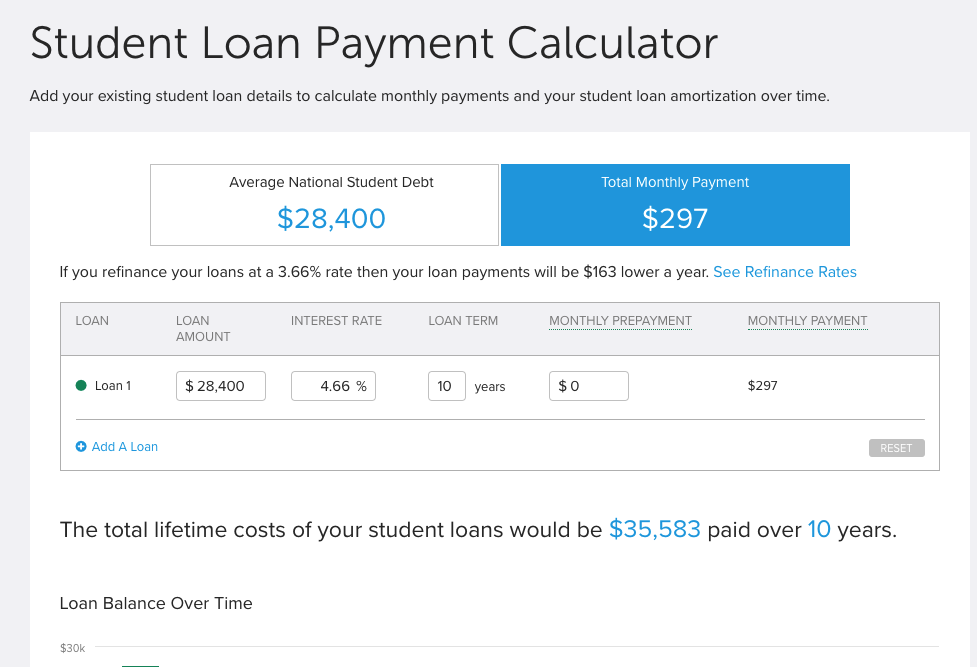
The calculator has gained links from the likes of NPR, Nasdaq, and Business Insider.
Write Guest Posts
Guest posting sites are a dime a dozen. So, it’s essential to use the same quality check mentioned above that you would on the link to evaluate your guest post target.
We identified 150 quality guest posting sites to help you better weed out the low-quality links.
There are some extra quality signals to be aware of when evaluating guest posts. Some signals include overt mentions of accepting guest posts for money.
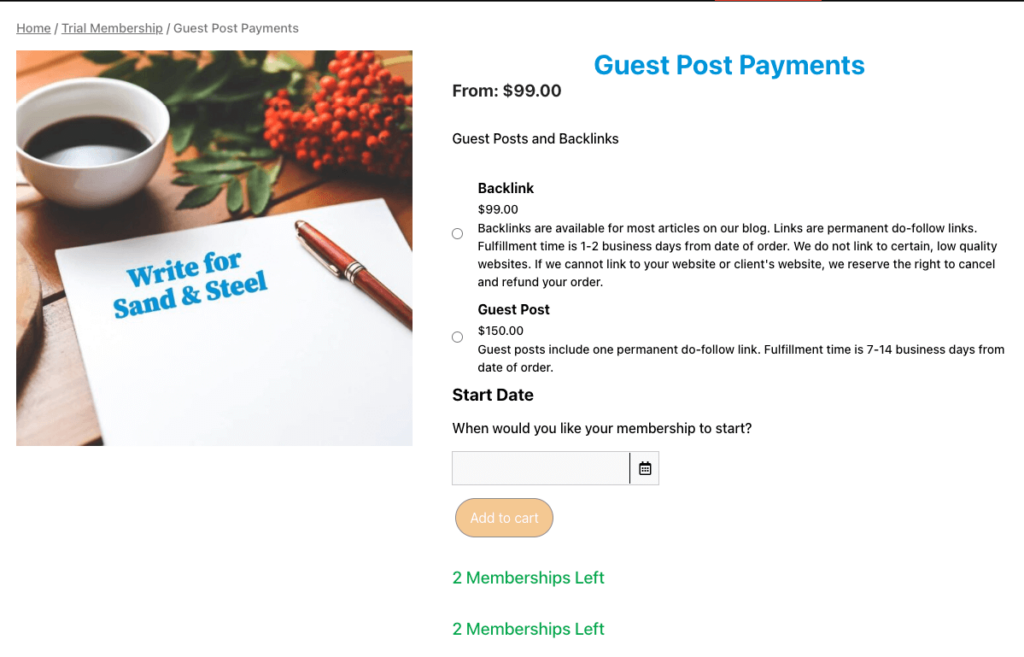
If a guest post site accepts any/all content just to make money, it is likely not paying too much attention to the quality.
Link Insertion
Getting your link inserted into an existing external post is a great way to control precisely where and how you get a backlink. You can run quality checks on the sites before you attempt a link insertion.

Note: Some people lump link insertion into guest posting because you can “insert” a link into the post that you create. Either way works.
Link Reclamation
If you had a quality link but lost it, you can regain it with a quick email.
Use a tool like Ahrefs Site Explorer to see “lost” backlinks. Sort by DR to ensure you are looking at quality sites.
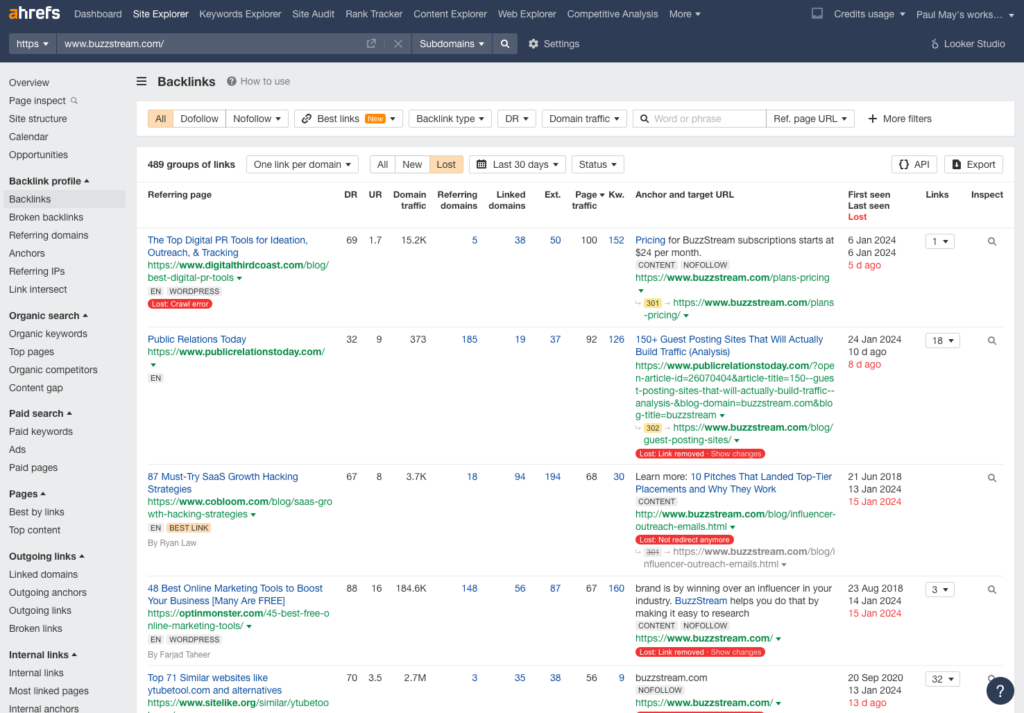
Unlinked Mentions
Use a service like Google Alerts or TalkWalker to find unlinked mentions of your brand online from quality websites. If you still need to, you can email them to request they include you.
(Use our email outreach templates for unlinked mention help.)
Brand Announcements
You can generate quality news links when something newsworthy occurs in your brand. First, ask yourself if your news is relevant to an external audience. If so, a press release is a great way to publicize your news.
Then, these press releases can yield links from high-quality, relevant industry news sites.
To determine if your news is worthy of a press release and coverage, look at some sites where you’d like coverage. Look at the kinds of news they share. If yours seems similar, you can probably get a quality link from them.
For example, say I was a construction-related brand and wanted to gain some links by reporting major company news. I’d look at a site like ForConstructionPros and see what kinds of news they share and try to tailor my pitch as such.
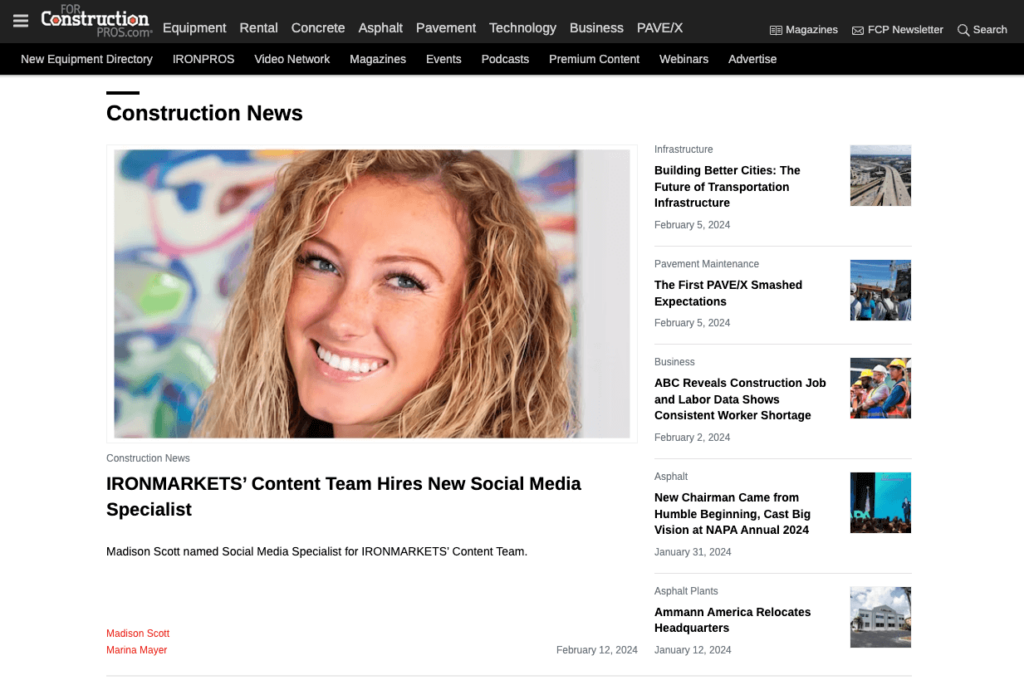
This example shows brand news about how IRONMARKETS has hired a new Social Media Specialist.
Reactive PR and Newsjacking
When news happens, you can position your brand/site as a thought leader, leading to quality backlinks.
Set up a reactive or newsjacking workflow by having a team member or members tap into your industry’s daily news. Use a platform like Google News and set up custom feeds.
If something comes up that a thought leader associated with your site can comment on, you can pitch that as a press release or directly to journalists in the space.
For example, if I were a health site, I might proactively provide a journalist a comment with tips or predictions about Alaskapox, given that several outlets have covered it in the past few hours, according to Google News.
Use examples of competitors’ success in reactive PR to convince the thought leaders at your site to open a line of communication for providing quotes to pitch.
Submitting Quotes on Request Platforms
Multiple platforms request quotes from thought leaders and experts in a field. Help A Reporter Out (HARO) is the most popular, but I also like Qwoted. It’s less crowded and provides more targetted requests.
In each, you sign up as a source and choose an industry. Then, you’ll receive quote requests from journalists and content writers. Usually, you’ll be able to assess a site’s overall quality.
Learn more about all of the link building strategies that you can use to build quality backlinks.
Frequently Asked Questions About Quality Links
Here are some frequently asked questions about quality links from our customers and around the web.
Can You Check if a Link Is Spammy?
There are multiple ways to check if a link is spammy. Always hover over links to preview the URL in your browser’s status bar before clicking. But if you want to evaluate the kinds of links you receive, you can use tools like the aforementioned Majestic’s Trust Flow or Moz’s Spam Score.
Google’s Safe Browsing Transparency Report is a free resource that will help identify individual pages that may be spammy. SpamHaus can also determine the status of IP addresses, domains, and senders.
If it looks spammy, it probably is.
What is the Best Type of Link?
The best type of link to help SEO and ranking is a high-quality, dofollow link from a reputable, relevant site within your industry.
However, it depends on your goals. The best type of link for a brand might be one built for brand exposure. These might not be dofollow, but they still offer great exposure for your brand from a reputable source.
For example, a link from Forbes.com is still incredibly valuable even though they are all nofollow.
How Do I Find Hidden Links?
To find hidden links on a webpage, use browser developer tools by right-clicking the page and selecting “Inspect” to view the HTML source code, where you can search for hidden link elements.
Chrome extensions like Link Klipper can extract all links on a page, helping identify ones that aren’t immediately visible. Additionally, running a site through Screaming Frog SEO Spider allows for a comprehensive crawl to detect hidden or cloaked links.
Chances are you won’t find hidden links unless you are dealing with gray or black hat methods of link building.

 End-to-end outreach workflow
End-to-end outreach workflow


 Check out the BuzzStream Podcast
Check out the BuzzStream Podcast